iOS Swift Anti-Jailbreak Bypass with Frida
Frida is a dynamic binary instrumentation framework that has been around for a while. In a nutshell, Frida allows reverse engineers to perform activities such as function hooking/trancing and runtime code modification. If your target is an iOS application, Frida provides you with powerful Objective-C API, making painless reverse engineering tasks. Unfortunately, out of the box, Frida lacks of Swift API, and some community contributions are outdated. Analysing Swift iOS applications with Frida hasn’t been an easy task for me so far. Fortunately, my friend r3dx0f provided me with some suggestions about how to approach the problem, and I will share with you what I learnt during this journey.
Swift Security Checks
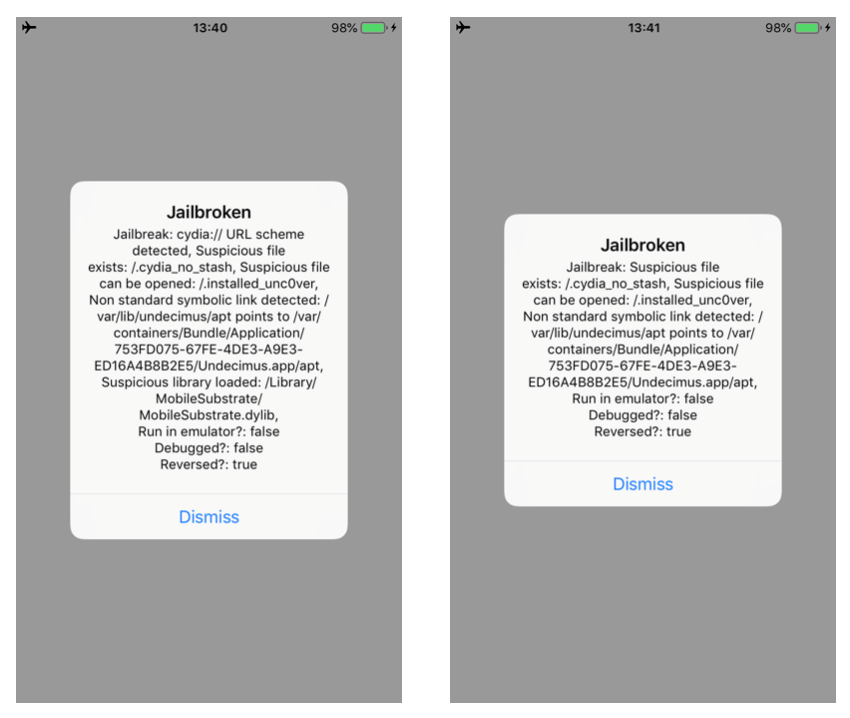
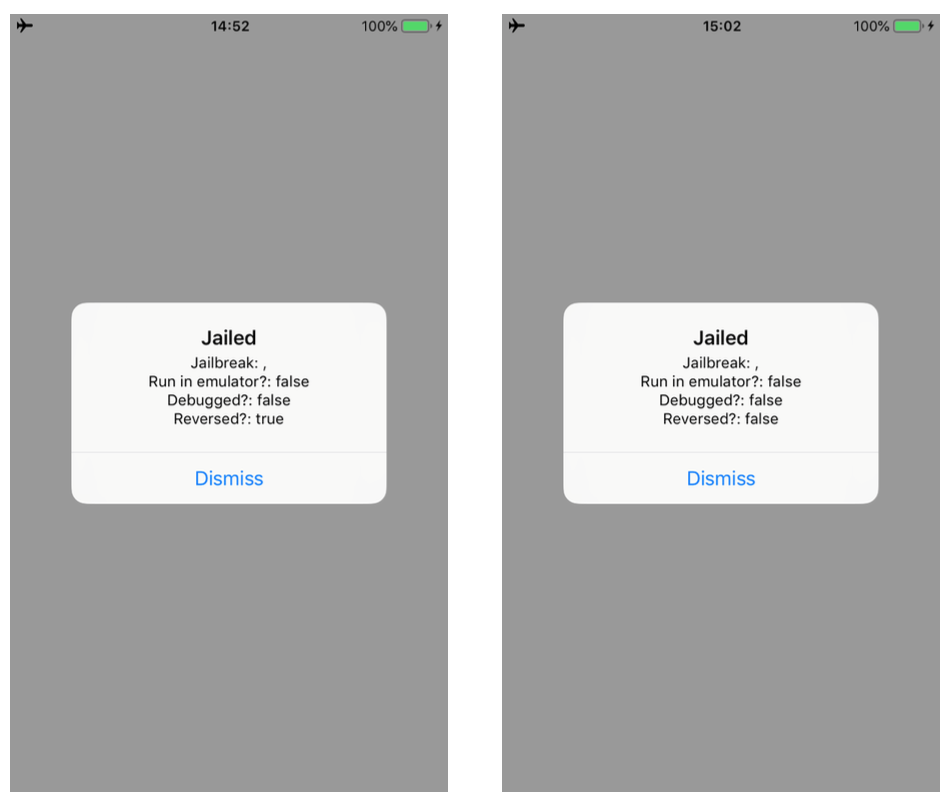
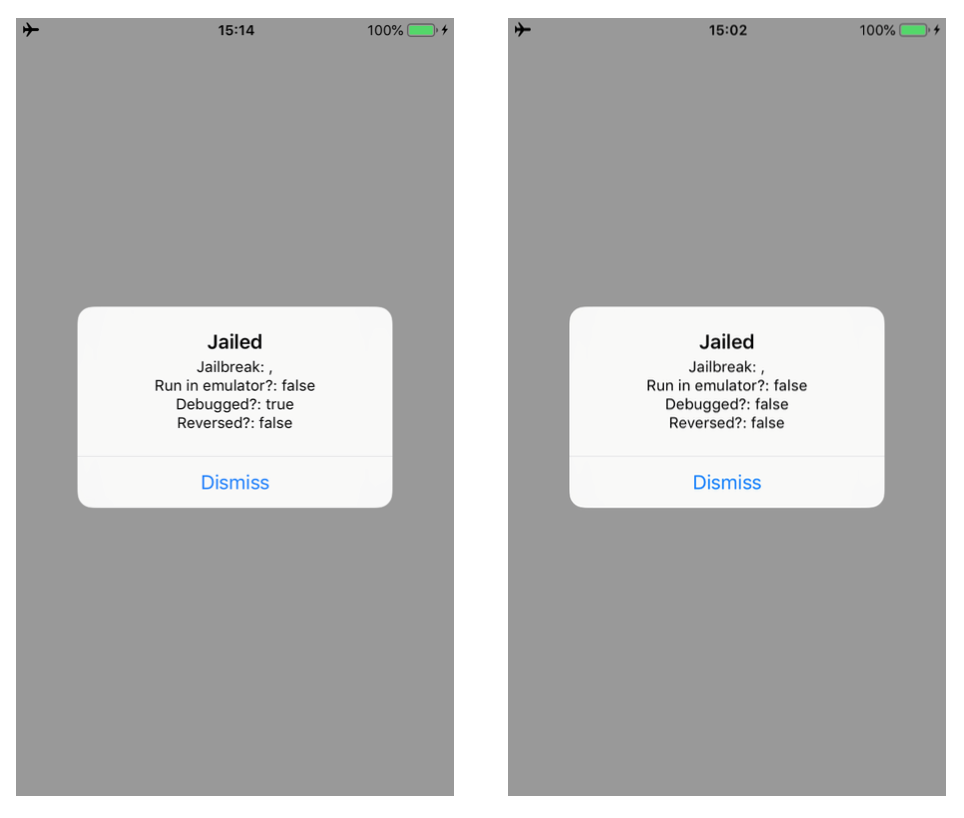
In this blogpost, I will describe how to bypass a number of jailbreak and reverse engineering detection mechanisms implemented within the IOSSecuritySuite. The aforementioned project is written in Swift and is hosted on Github. However, we will perform the analysis against a non-stripped iOS application which implements such library. The analysis will be conducted without the support of the source code in order to simulate a real-life scenario. When the application is executed, it shows the message below, telling us that our iPhone is jailbroken. Some suspicious files are found and the application is considered “reversed”.
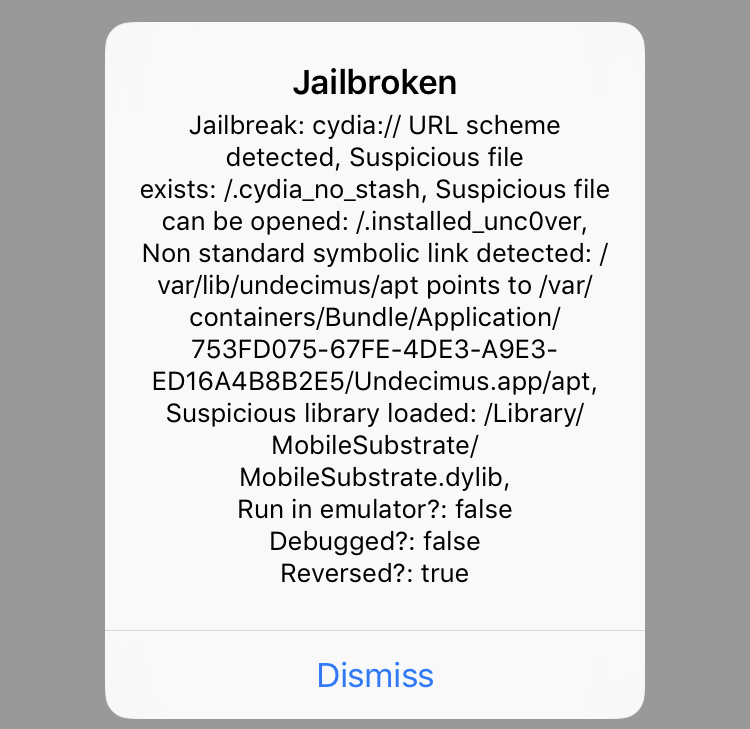
We have two modules defined within the binary:
- FrameworkClientApp
- IOSSecuritySuite
Because we know that the IOSSecuritySuite modules contains the jailbreak detection mechanism logic, we will reverse it first.
Reverse Engineering
When I’m looking for jailbreak detection mechanisms, I usually start searching for strings and functions containing the word “jailbr” (jail, jailbreak or jailbroken) or “root”. We have a lot of matches as shown below:
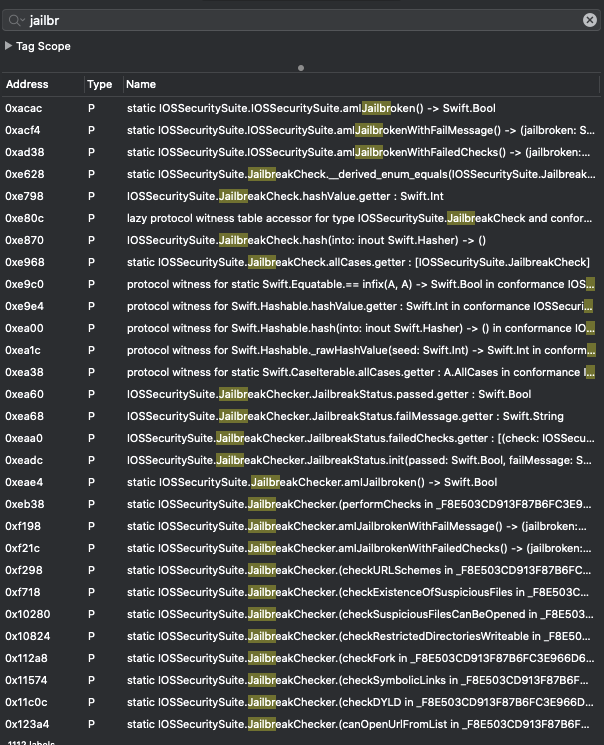
My first goal is to hook each function and see if it does affect the alert message that we saw before.
Bypass canOpenUrlFromList
The first function we are going to analyse is _$s16IOSSecuritySuite16JailbreakCheckerC18canOpenUrlFromList33_F8E503CD913F87B6FC3E966D69D 813ABLL10urlSchemesSb6passed_SS11failMessagetSaySSG_tFZ.
By reversing it, we can see the canOpenURL method call at the address offset 0x126bc. According with the AArch64 ABI, the x0 register will contain the value returned from the function call. This function usually tries to open suspicious URL scheme such as “cydia://” in order to identify jailbreak artefact. When it founds any suspicious file, the function returns “true”. Because the value returned is a Boolean it should contain the values 0x01 (true) or 0x00 (false), therefore we have to change it to 0x00 in order to bypass this check.
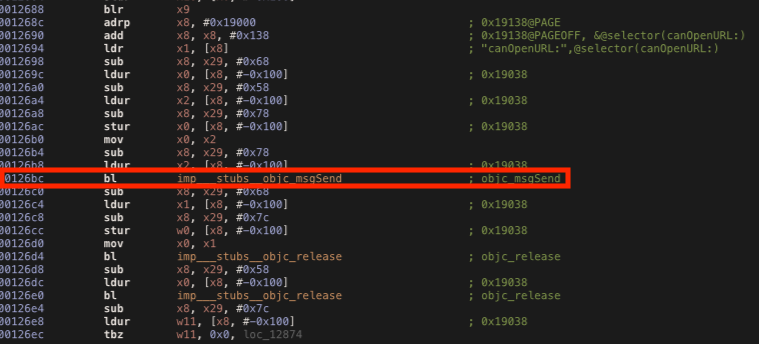
We can use Frida’s Module.getBaseAddress() function to obtain the base address where the library is loaded in memory (Frida calculate the ASLR Shift for us) and then we have to add the 0x126c offset to it. Then we ask Frida to hook and replace the code at that specific address (baseAddress+offset). Our implementations will change the x0 register value from 0x01 (true) to 0x00 (false). In Frida we can access register’s values by using the this.context object.
Frida Code
var targetModule = 'IOSSecuritySuite';
var addr = ptr(0x126c0);
var moduleBase = Module.getBaseAddress(targetModule);
var targetAddress = moduleBase.add(addr);
Interceptor.attach(targetAddress, {
onEnter: function(args) {
if(this.context.x0 == 0x01){
this.context.x0=0x00
console.log("Bypass canOpenUrlFromList");
}
},
});
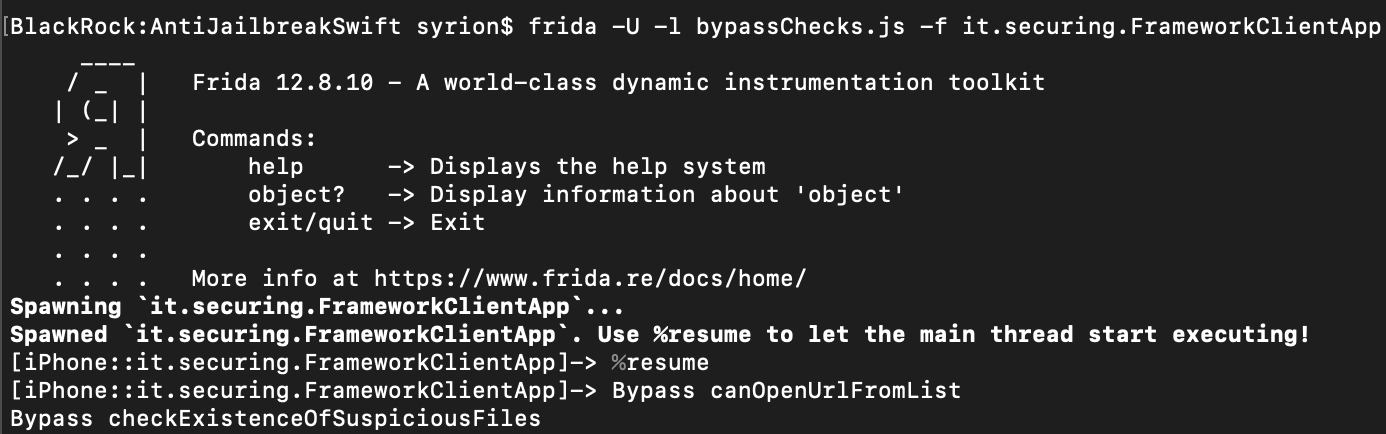
Running the script, we can see that the target instruction is reached and the check is bypassed as shown in the images below.
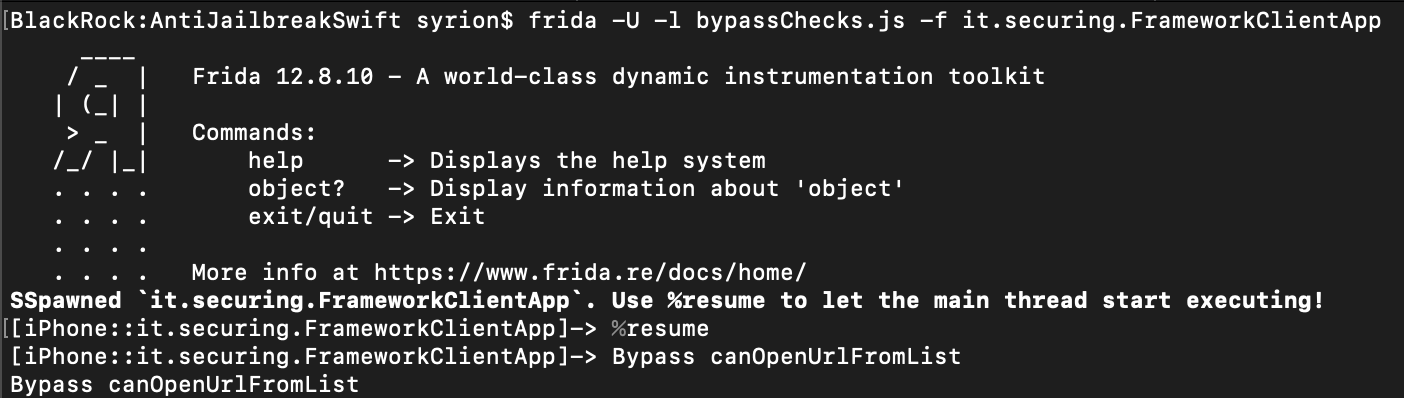
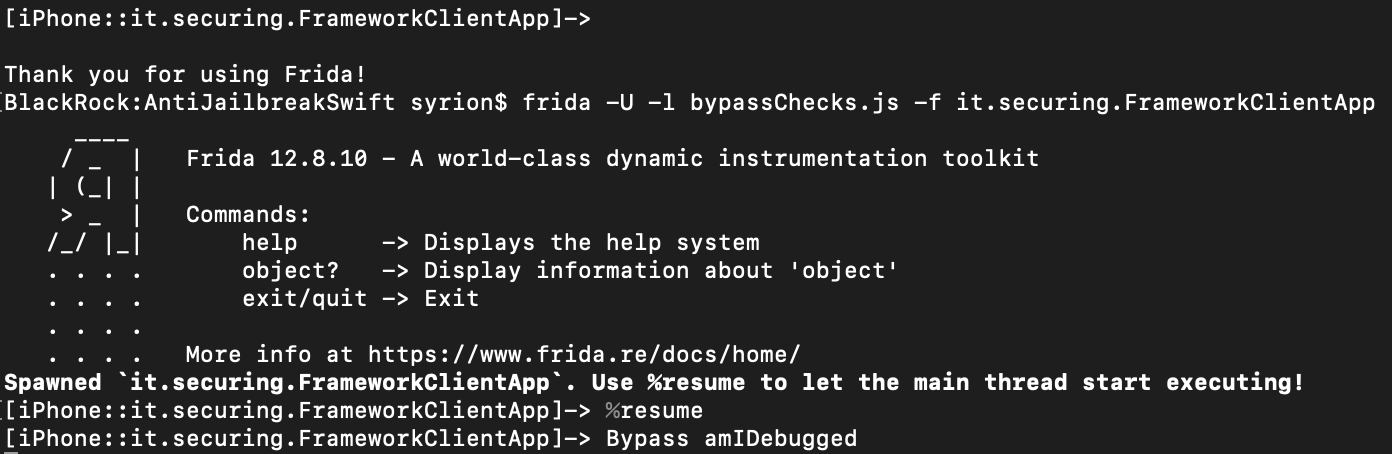
N.B. During the analysis it was observed that some Swift functions defined within the IOSSecuritySuite library, executed Objective-C code by “bridging” them. It should be noted that in such circumstances, controls can also be bypassed by using the “ObjC” object defined within Frida’s API.
Bypass checkExistenceOfSuspiciousFiles
Function: _$s16IOSSecuritySuite16JailbreakCheckerC31checkExistenceOfSuspiciousFiles33_F8E503CD913F87 B6FC3E966D69D813ABLLSb6passed_SS11failMessagetyFZ
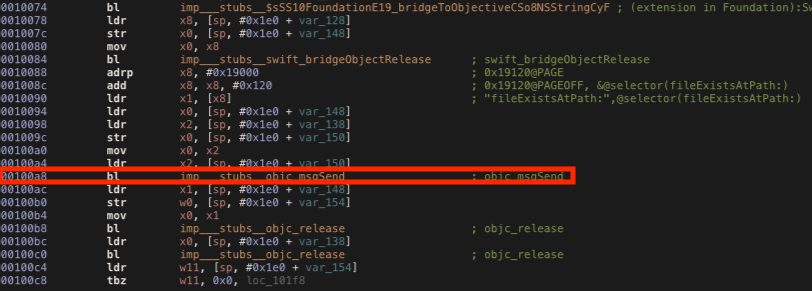
In the disassembled code below we can see that the function calls the fileExistsAtPath method at the offset address 0x100a8, so we need to change the return value as we did before.
Using the same Frida code we can set the new target address, and bypass the check.
Frida Code
addr = ptr(0x100ac);
moduleBase = Module.getBaseAddress(targetModule);
targetAddress = moduleBase.add(addr);
Interceptor.attach(targetAddress, {
onEnter: function(args) {
if(this.context.x0 == 0x01){
this.context.x0=0x00
console.log("Bypass checkExistenceOfSuspiciousFiles");
}
},
});
Running the updated script, we can bypass the two methods. As shown in the images below. Moreover, the message in the alert box will change as well.
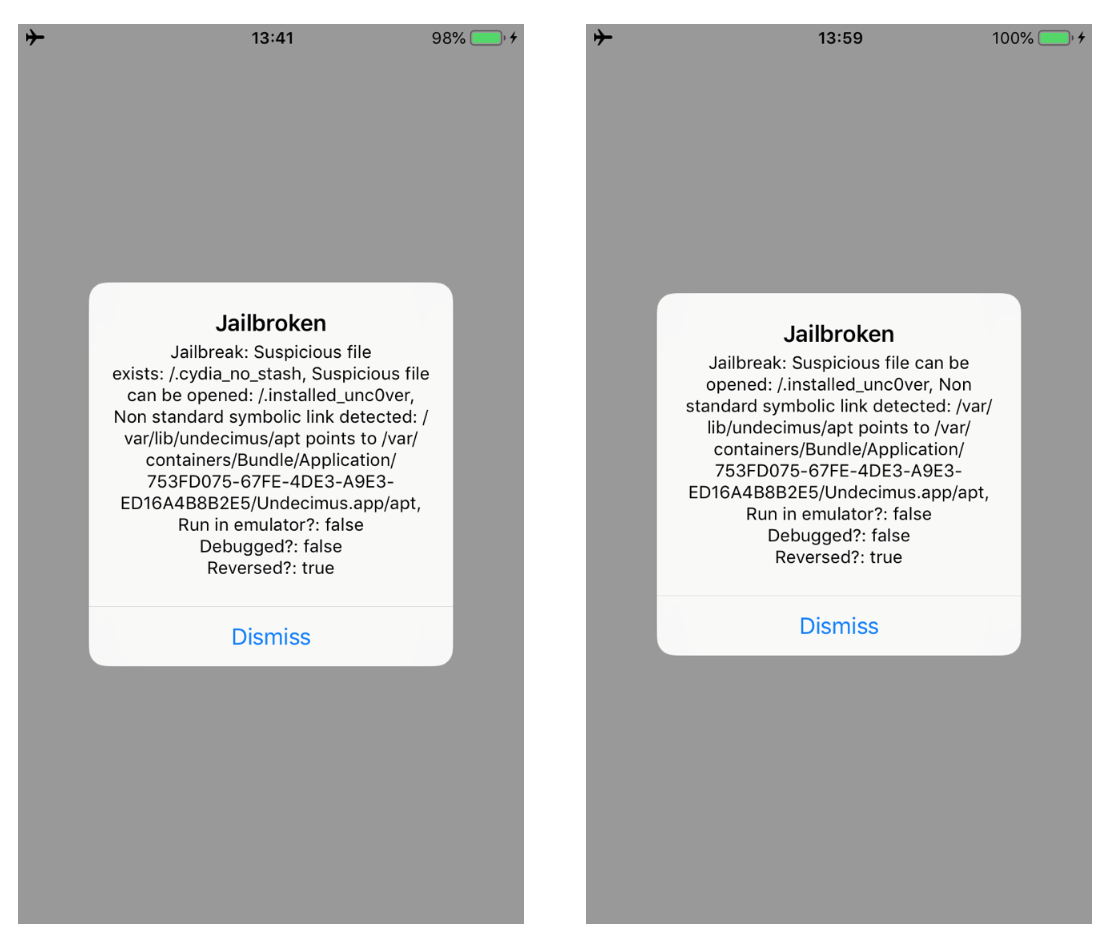
Bypass checkSuspiciousFilesCanBeOpened
Function: _$s16IOSSecuritySuite16JailbreakCheckerC31checkSuspiciousFilesCanBeOpened33_F8E503CD913F87 B6FC3E966D69D813ABLLSb6passed_SS11failMessagetyFZ
As we can see in the disassembled code below, the isReadableFileAtPath method is called at the offset address 0x1064c and the return value is stored in the x0 register as usual.
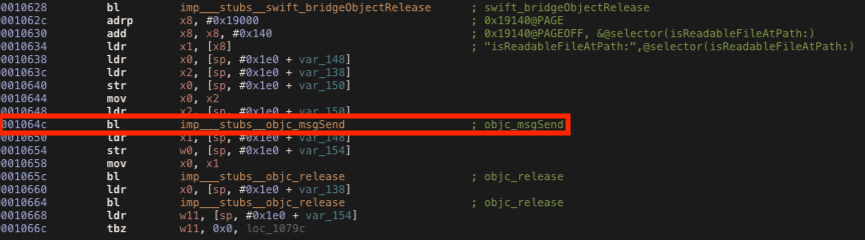
Using the same script with the new address we can bypass the check.
Frida Code
addr = ptr(0x10650);
moduleBase = Module.getBaseAddress(targetModule);
targetAddress = moduleBase.add(addr);
Interceptor.attach(targetAddress, {
onEnter: function(args) {
if(this.context.x0 == 0x01){
this.context.x0=0x00
console.log("Bypass checkSuspiciousFilesCanBeOpened");
}
},
});
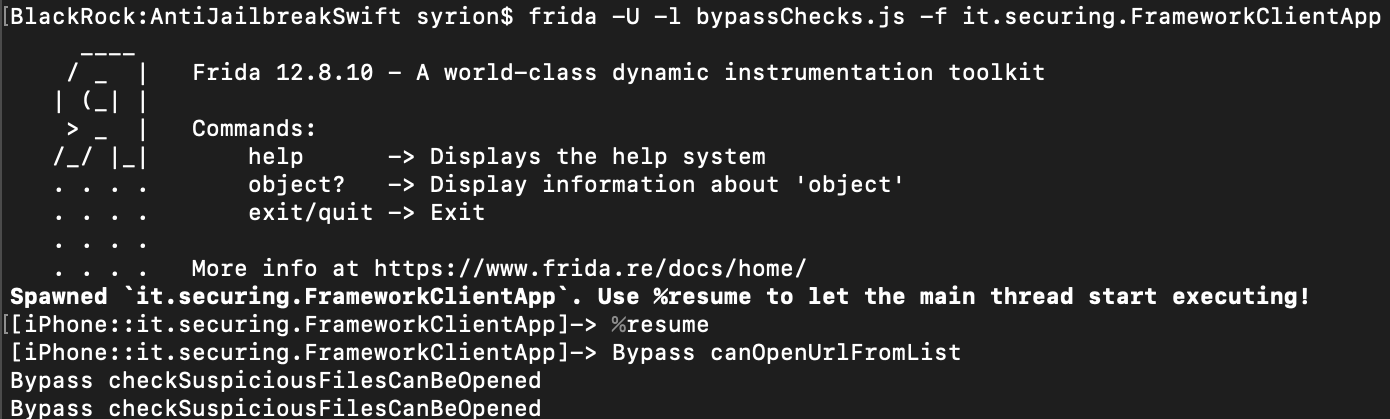
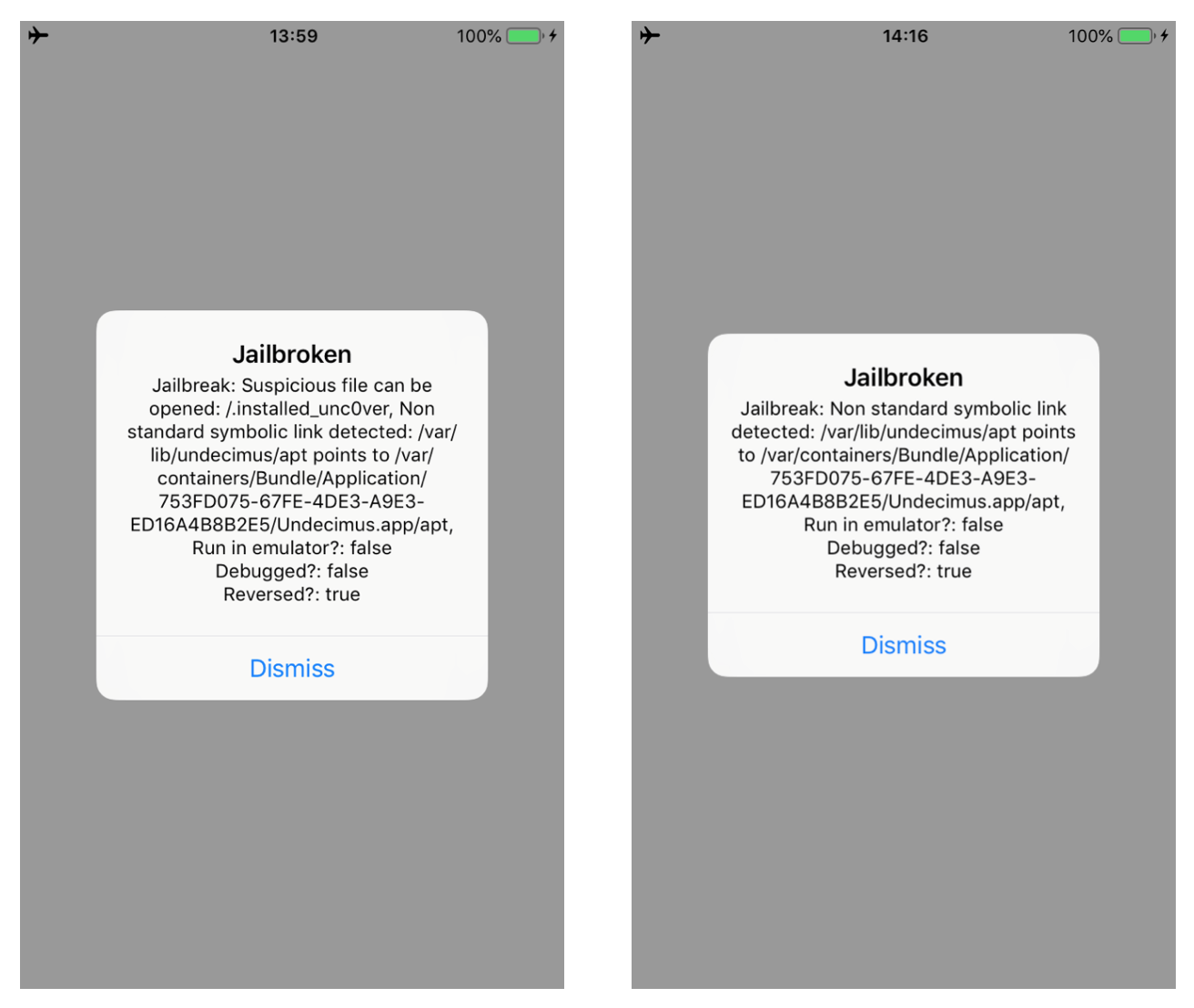
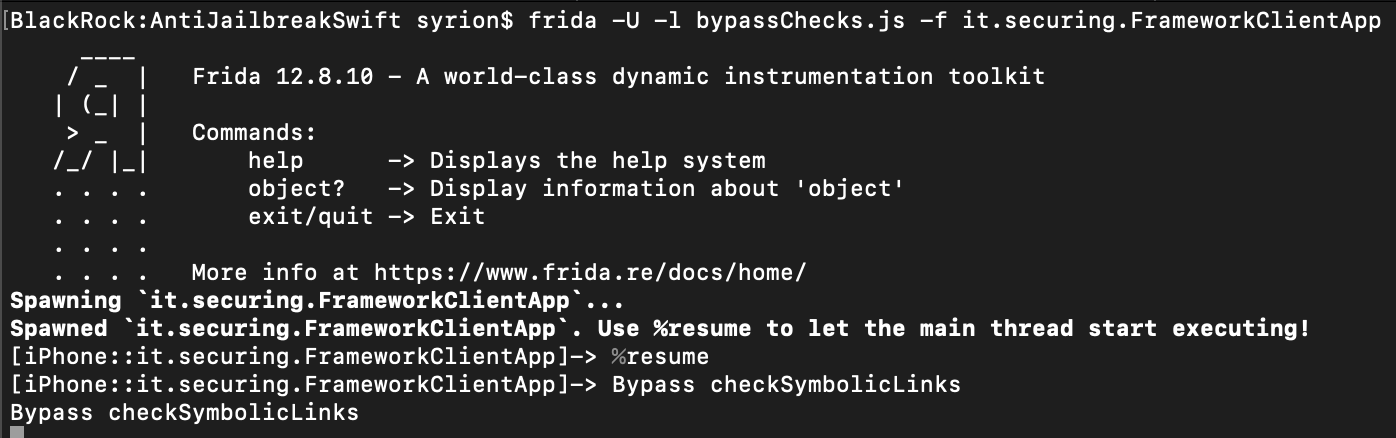
Bypass checkSymbolicLinks
Function: _$s16IOSSecuritySuite16JailbreakCheckerC18checkSymbolicLinks33_F8E503CD913F87B6FC3E966 D69D813ABLLSb6passed_SS11failMessagetyFZ
Our iPhone is still recognized as “jailbroken”, so we need to bypass other methods. As we can see below, the destinationOfSymbolicLinkAtPath method is called at the offset address 0x118ac, so we can modify the x0 register by replacing the its value with 0x00 as we did before.
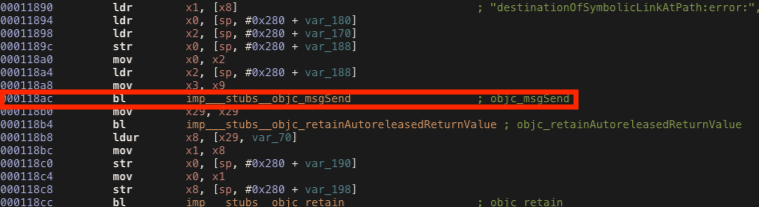
Using the same script we can change the return value contained in the x0 register.
Frida Code
addr = ptr(0x118b0);
moduleBase = Module.getBaseAddress(targetModule);
targetAddress = moduleBase.add(addr);
Interceptor.attach(targetAddress, {
onEnter: function(args) {
if(this.context.x0 != 0x00){
this.context.x0 = 0x00
console.log("Bypass checkSymbolicLinks");
}
},
});
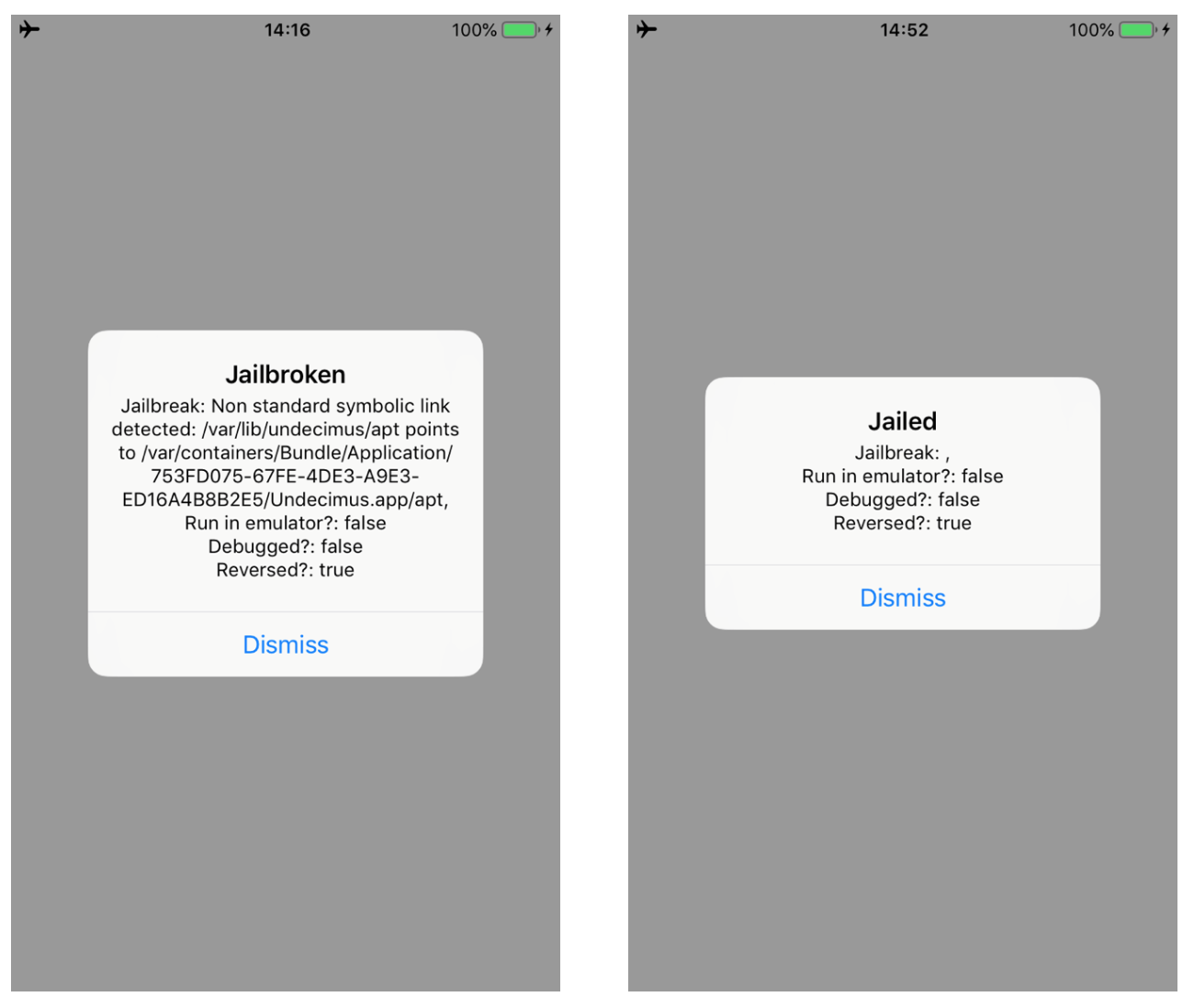
We successfully bypassed all the Anti-Jailbreak checks.
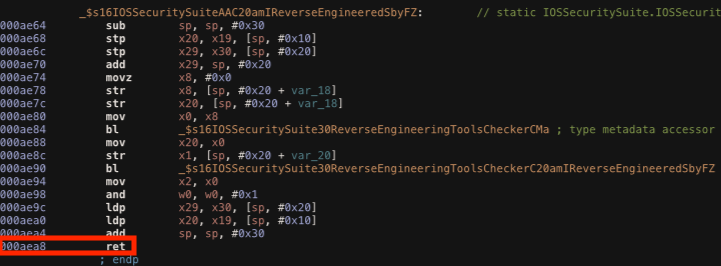
Bypass amIReversed
Function: _$s16IOSSecuritySuiteAAC20amIReverseEngineeredSbyFZ
The method amIReversed checks if the application is debugged or tampered using instrumentation tools like Frida. Again, we can change its return value contained in the x0 register, before the RET instruction is executed at the offset address 0xaea8.
Frida Code
addr = ptr(0xaea8);
moduleBase = Module.getBaseAddress(targetModule);
targetAddress = moduleBase.add(addr);
Interceptor.attach(targetAddress, {
onEnter: function(args) {
if(this.context.x0 == 0x01){
this.context.x0=0x00
console.log("Bypass amIReverseEngineered");
}
},
});
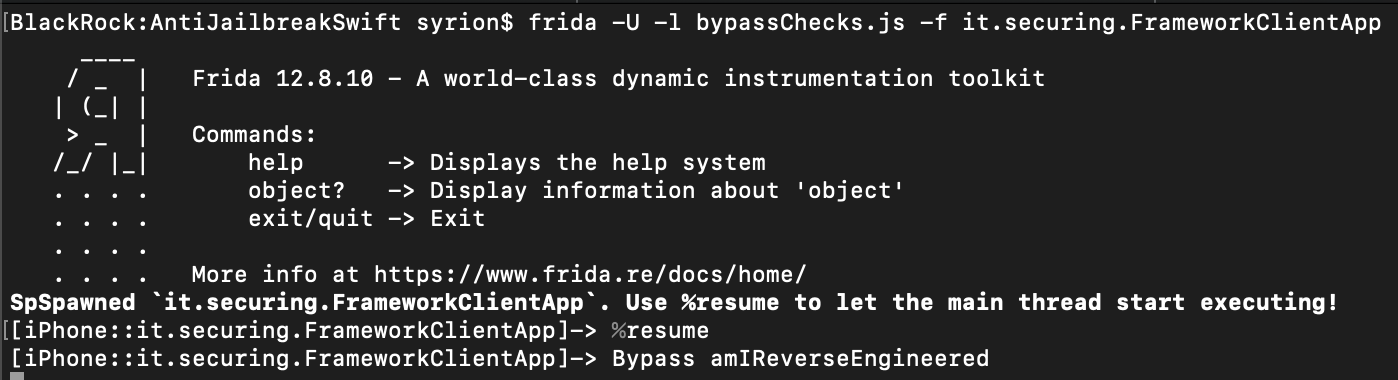
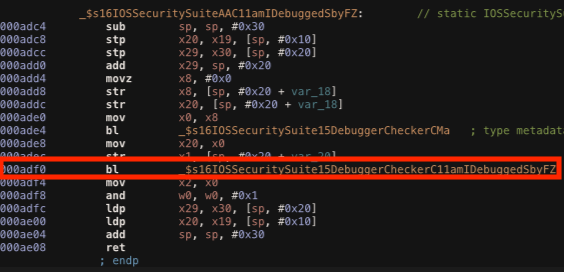
Bypass AmIDebugged
Function: _$s16IOSSecuritySuiteAAC11amIDebuggedSbyFZ
The function AmIDebugged checks if the application is debugged, following the method call, we can see there is another method _$s16IOSSecuritySuite15DebuggerCheckerC11amIDebuggedSbyFZ looking for a debugger using sysctl and getPid (same used in my previos post).
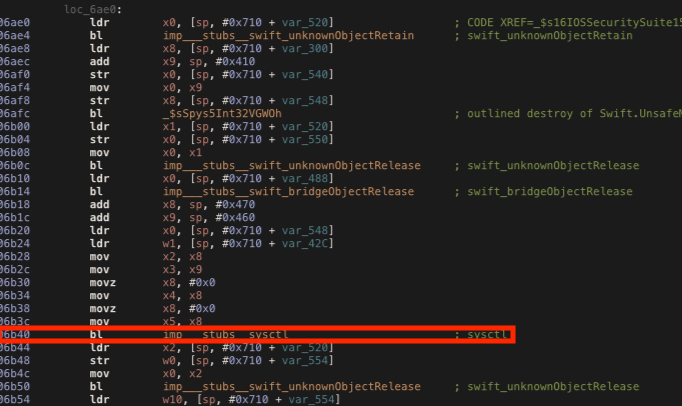
If we try to debug the application, the check will return true but we can hook the ret instruction at address 0xae08 and change the return value contained in x0 to 0x00 with the following Frida script.
Frida Code
addr = ptr(0xae08);
moduleBase = Module.getBaseAddress(targetModule);
targetAddress = moduleBase.add(addr);
Interceptor.attach(targetAddress, {
onEnter: function(args) {
if(this.context.x0 == 0x01){
this.context.x0=0x00
console.log("Bypass amIDebugged");
}
},
});
Bypass amIRunInEmulator
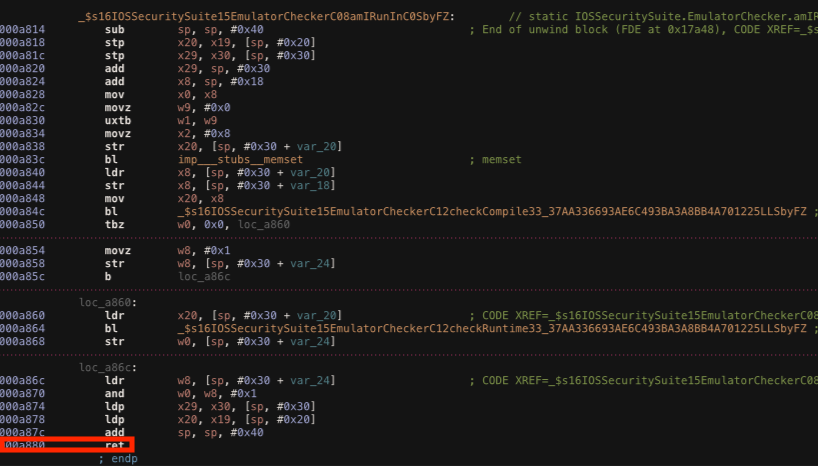
Function: _$s16IOSSecuritySuite15EmulatorCheckerC08amIRunInC0SbyFZ
Because the application is running on a real iPhone, the amIrunInEmulator check can’t be triggered, therefore what we can do is to inject a true value and let the application believe that is running in an emulator. The image below shows the method. As always, we have to change the x0 register value before the RET instruction at the offset address 0xa880 is executed.
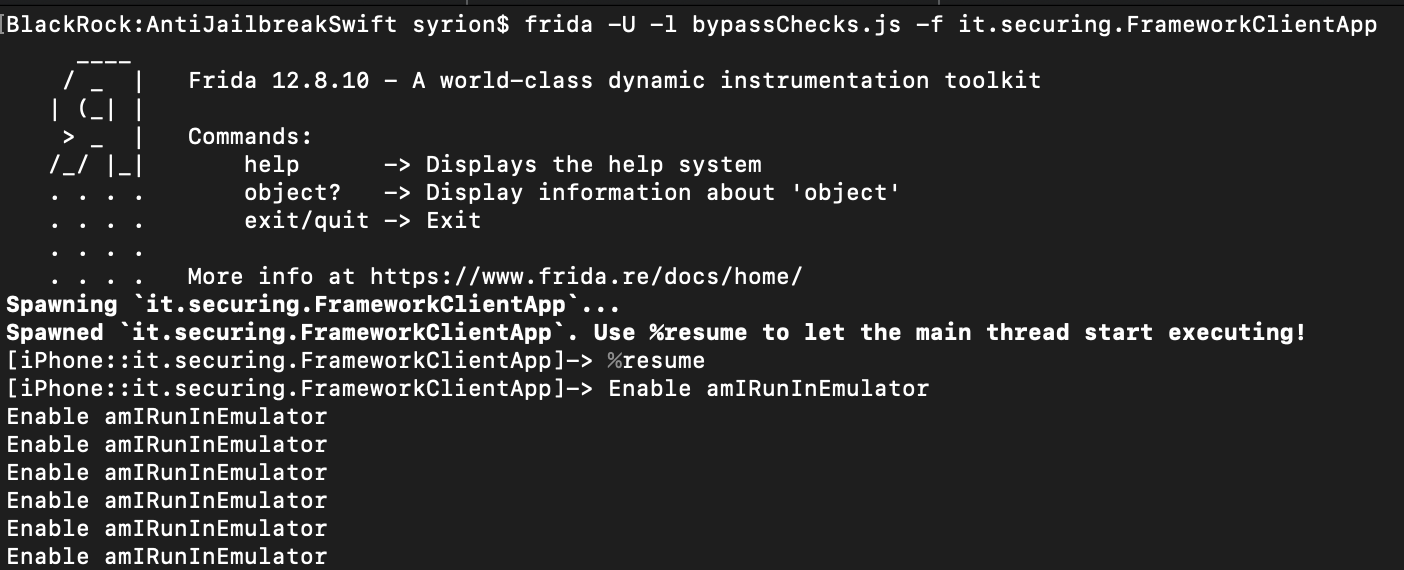
We can “enable” the emulator with the following Frida script.
Frida Code
addr = ptr(0xa880);
moduleBase = Module.getBaseAddress(targetModule);
targetAddress = moduleBase.add(addr);
Interceptor.attach(targetAddress, {
onEnter: function(args) {
if(this.context.x0 == 0x00){
this.context.x0=0x01
console.log("Enable amIRunInEmulator");
}
},
});
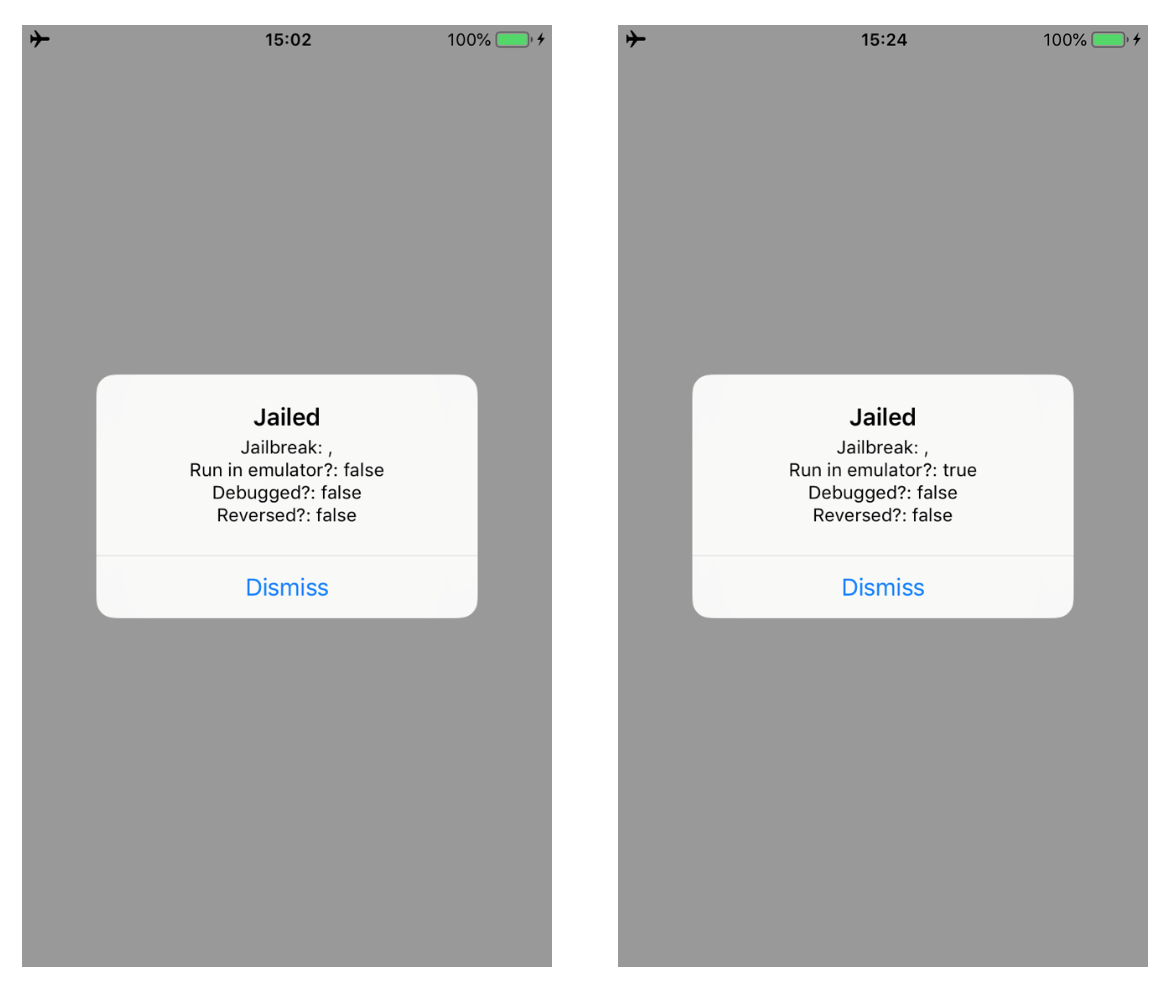
Change the “Jailed” string
Finally, I wanted to change “Jailed” string for fun. However, its address is no writable so we can’t modify its value. What we can do, is creating our own string and put its address in the register that point to the string message. In order to do so, we need to reverse the FrameworkClientApp module. In the _$s18FrameworkClientApp14ViewControllerC13viewDidAppearyySbF methods, we can find the instruction where the “Jailed” string address is put into the x0 register . We can see it at address 0x4348.
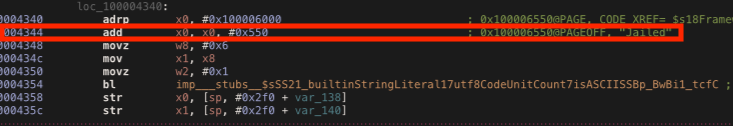
We can create our own string and put its address into the x0 register after the instruction at address 0x4348.
Frida Code
targetModule = 'FrameworkClientApp';
addr = ptr(0x04348);
moduleBase = Module.getBaseAddress(targetModule);
targetAddress = moduleBase.add(addr);
var myMessage = Memory.allocUtf8String("Br0k3n")
Interceptor.attach(targetAddress, {
onEnter: function(args) {
this.context.x0 = myMessage;
},
});
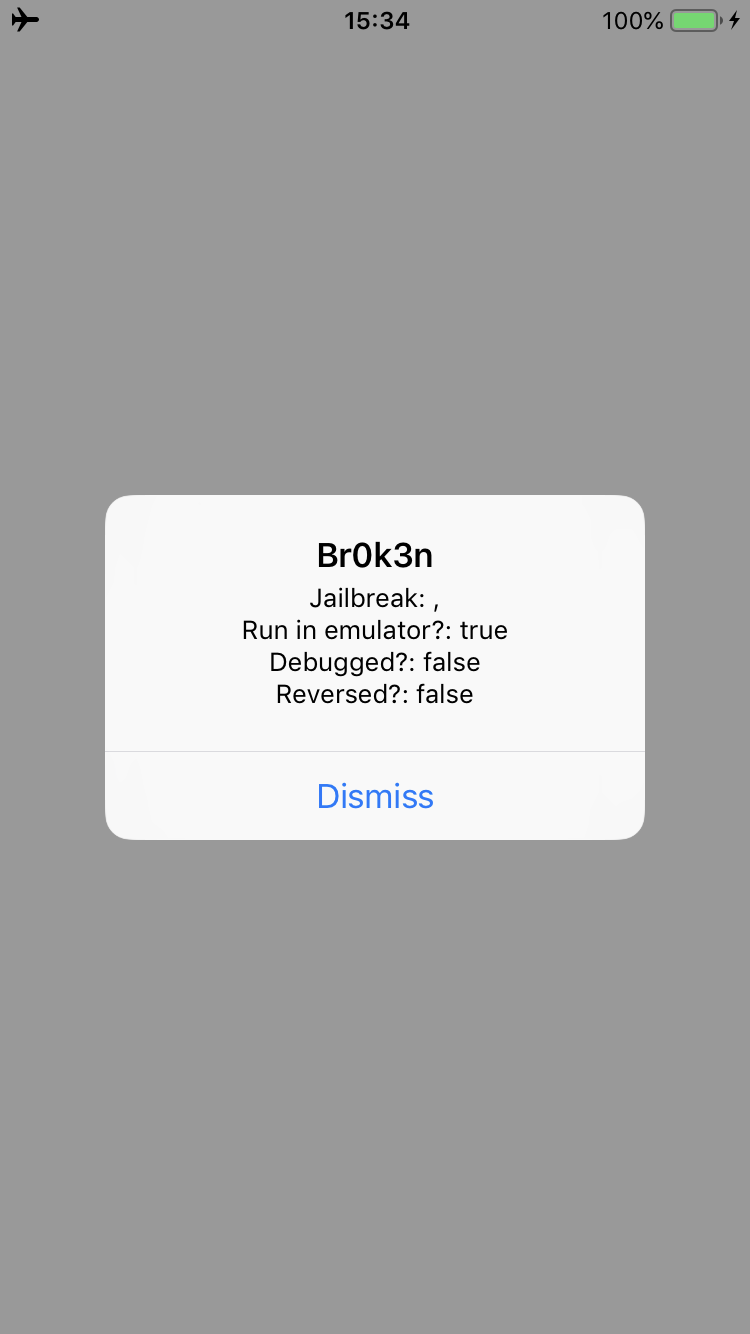
The “Br0k3n” string is very l33t ;-) This is the complete Frida script (which potentially can be written in a better way, so I will let this to you as exercise).
var targetModule = 'IOSSecuritySuite';
var addr = ptr(0x126c0);
var moduleBase = Module.getBaseAddress(targetModule);
var targetAddress = moduleBase.add(addr);
Interceptor.attach(targetAddress, {
onEnter: function(args) {
if(this.context.x0 == 0x01){
this.context.x0=0x00
console.log("Bypass canOpenUrlFromList");
}
},
});
addr = ptr(0x100ac);
moduleBase = Module.getBaseAddress(targetModule);
targetAddress = moduleBase.add(addr);
Interceptor.attach(targetAddress, {
onEnter: function(args) {
if(this.context.x0 == 0x01){
this.context.x0=0x00
console.log("Bypass checkExistenceOfSuspiciousFiles");
}
},
});
addr = ptr(0x10650);
moduleBase = Module.getBaseAddress(targetModule);
targetAddress = moduleBase.add(addr);
Interceptor.attach(targetAddress, {
onEnter: function(args) {
if(this.context.x0 == 0x01){
this.context.x0=0x00
console.log("Bypass checkSuspiciousFilesCanBeOpened");
}
},
});
addr = ptr(0x118b0);
moduleBase = Module.getBaseAddress(targetModule);
targetAddress = moduleBase.add(addr);
Interceptor.attach(targetAddress, {
onEnter: function(args) {
if(this.context.x0 != 0x00){
this.context.x0 = 0x00
console.log("Bypass checkSymbolicLinks");
}
},
});
addr = ptr(0xaea8);
moduleBase = Module.getBaseAddress(targetModule);
targetAddress = moduleBase.add(addr);
Interceptor.attach(targetAddress, {
onEnter: function(args) {
if(this.context.x0 == 0x01){
this.context.x0=0x00
console.log("Bypass amIReverseEngineered");
}
},
});
addr = ptr(0xae08);
moduleBase = Module.getBaseAddress(targetModule);
targetAddress = moduleBase.add(addr);
Interceptor.attach(targetAddress, {
onEnter: function(args) {
if(this.context.x0 == 0x01){
this.context.x0=0x00
console.log("Bypass amIDebugged");
}
},
});
addr = ptr(0xa880);
moduleBase = Module.getBaseAddress(targetModule);
targetAddress = moduleBase.add(addr);
Interceptor.attach(targetAddress, {
onEnter: function(args) {
if(this.context.x0 == 0x00){
this.context.x0=0x01
console.log("Enable amIRunInEmulator");
}
},
});
targetModule = 'FrameworkClientApp';
addr = ptr(0x04348);
moduleBase = Module.getBaseAddress(targetModule);
targetAddress = moduleBase.add(addr);
var myMessage = Memory.allocUtf8String("Br0k3n")
Interceptor.attach(targetAddress, {
onEnter: function(args) {
this.context.x0 = myMessage;
},
});
Conclusion
As we have seen, Frida provides a very powerful way to attach each arm instruction and interact with register and memory. Its documentation is very clear and full of examples. I hope you enjoined it. If you find any mistakes in my write-up please contact me and I will be more than happy to fix them.

